示例代码
先给出第一课学习的代码。
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Device : NSObject
-(void) wakeUp;
-(void) setPasswd: (int)input;
-(void) verifyPasswd;
-(int) getPasswd;
@end
@implementation Device {
int passwd;
}
- (void)wakeUp{
NSLog(@"The device was woken up.");
}
-(void)setPasswd:(int)input {
passwd = input;
}
-(void)verifyPasswd {
if( passwd == 1111 )
NSLog(@"The password of this device is correct.");
else
NSLog(@"The password of this device is incorrect!");
}
-(int) getPasswd {
return passwd;
};
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
Device *iPhone = [[Device alloc] init];
Device *iPad = [[Device alloc] init];
[iPhone wakeUp];
[iPhone setPasswd:1000];
[iPhone verifyPasswd];
NSLog(@"The password of iPhone is %i.",[iPhone getPasswd]);
[iPad wakeUp];
[iPad setPasswd:1111];
[iPad verifyPasswd];
NSLog(@"The password of iPad is %i.",[iPad getPasswd]);
}
return 0;
}运行结果如下:
2020-03-21 12:20:14.658475+0800 DemoProgram[26195:134286] The device was woken up.
2020-03-21 12:20:14.658766+0800 DemoProgram[26195:134286] The password of this device is incorrect!
2020-03-21 12:20:14.658820+0800 DemoProgram[26195:134286] The password of iPhone is 1000.
2020-03-21 12:20:14.658854+0800 DemoProgram[26195:134286] The device was woken up.
2020-03-21 12:20:14.658875+0800 DemoProgram[26195:134286] The password of this device is correct.
2020-03-21 12:20:14.658893+0800 DemoProgram[26195:134286] The password of iPad is 1111.
Program ended with exit code: 0代码解释
@interface 部分用于描述类和类的方法;@implementation 部分用于描述类对象的实例变量存储的数据,同时实现了接口中声明的方法;剩下代码实现了程序的功能。
alloc
alloc即 allocate,目的是为新创建的对象分配内存存储空间。alloc保证对象的所有实例变量都变成初始状态,但不意味着对象完成了初始化工作,完成初始化工作需要使用init完成。
alloc 直接调用了另一个私有方法 id _objc_rootAlloc(Class cls)。
+ (id)alloc {
return _objc_rootAlloc(self);
}id _objc_rootAlloc(Class cls)调用了callAlloc(cls, false/*checkNil*/, true/*allocWithZone*/),即 NSObject 对 callAlloc 的实现.
id _objc_rootAlloc(Class cls) {
return callAlloc(cls, false/*checkNil*/, true/*allocWithZone*/);
}继续研究callAlloc(Class cls, bool checkNil, bool allocWithZone=false)
static id callAlloc(Class cls, bool checkNil, bool allocWithZone=false) {
id obj = class_createInstance(cls, 0);
return obj;
}
id class_createInstance(Class cls, size_t extraBytes) {
return _class_createInstanceFromZone(cls, extraBytes, nil);
}对象初始化中最重要的操作都在 _class_createInstanceFromZone 方法中执行:
static id _class_createInstanceFromZone(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, void *zone, bool cxxConstruct = true, size_t *outAllocatedSize = nil) {
size_t size = cls->instanceSize(extraBytes);
id obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
if (!obj) return nil;
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor);
return obj;
}init
init用于初始化类的实例变量,iPhone = [iPhone init]; 初始化了一个特殊的 Device 对象,然而他没有发送给类,而是发送给了类的一个实例。init方法也可以返回被初始化的对象。
NSObject 的 - init 方法调用了 _objc_rootInit 并返回了当前对象:
- (id)init {
return _objc_rootInit(self);
}
id _objc_rootInit(id obj) {
return obj;
}声明方法
Objective-C 中声明的语法较为特别,方法名以冒号结束告诉编译器该方法有参数,在一对圆括号内指定参数的类型,与指定返回值的方法类似,和 C 类似整个声明以一个分号结束,给出一张图展示声明方法。
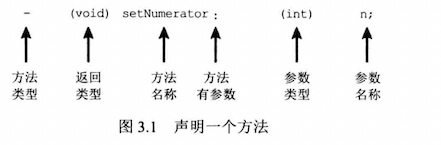
规范注意
流程为在@interface部分声明方法,并在@implementation部分定义它们,可使用冒号指明ParentClassName,与在@interface部分使用冒号一样:
@implementation Device: NSObject但通常不这么做。
new方法可以将alloc和init的操作结合起来,用两步来实现创建和初始化的方式可以在概念上理解正在发生两个不同的事件:首先创建对象,然后对它初始化。
即以下三种方式意义相同。
Device *iPhone = [[Device alloc] init];
Device *iPhone;
iPhone = [Device alloc];
iPhone = [iPhone init];
Device *iPhone = [ Device new];